Python數值型別資料、運算及字串(Python自動化測試入門2)
本篇內容較長,介紹了Python數值型別、運算以及字串的一些操作,逐步的學習過程中也會涉及到面試常考題,後續我會整理一篇面試常見題。
一、Python運運算元
Python運運算元包含算數運運算元、賦值運運算元、比較運運算元、邏輯運運算元四種
1.1 算數運運算元
算數運運算元就是簡單的加、減、乘、除
1.1.1 加
num1 = 100
num2 = 99
sum = num1 + num2
print(sum)
執行結果:
C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python37\python.exe E:/python程式小專案/day17/one.py
199
1.1.2 減
num1 = 100
num2 = 99
dec = num1 - num2
print(dec)
運算結果:
C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python37\python.exe E:/python程式小專案/day17/one.py
1
1.1.3 乘
num1 = 100
num2 = 99
mul = num1 * num2
print(mul)
運算結果:
C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python37\python.exe E:/python程式小專案/day17/one.py
9900
1.1.4 除
num1 = 100
num2 = 99
div = num1 * num2
print(div)
運算結果:
C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python37\python.exe E:/python程式小專案/day17/one.py
1.0101010101010102
1.2 賦值運運算元
賦值運運算元包含 += 、-= 、*= 、/=
1.2.1 +=
sum+=100 ,即等於sum = sum + 100
其餘的賦值運運算元同理
1.3 比較運運算元
比較運運算元包含 == 、!= 、 > 、< 、>= 、<=
比較運運算元的執行結果是布林值(False、True)
num1 = 100
num2 = 99
print(num1 == num2)
print(num1 != num2)
print(num1 >= num2)
print(num1 <= num2)
print(num1 < num2)
print(num1 > num2)
執行結果:
C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python37\python.exe E:/python程式小專案/day17/one.py
False
True
True
False
False
True
1.4 邏輯運運算元
邏輯運運算元包含與(and)、或(or)、非(not)三種
邏輯運運算元的執行結果也是布林值(False、True)
1.4.1 與(and)
所有條件為真,結果才為真
user_age = int(input('請輸入你的年齡:'))
user_city = input('請輸入你的城市:')
res = user_age < 30 and user_city == '上海'
print(res)
執行結果:
C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python37\python.exe E:/python程式小專案/day17/one.py
請輸入你的年齡:31
請輸入你的城市:上海
False
1.4.2 或(or)
任意條件為真,則結果為真
user_age = int(input('請輸入你的年齡:'))
user_city = input('請輸入你的城市:')
res = user_age < 30 or user_city == '上海'
print(res)
執行結果:
C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python37\python.exe E:/python程式小專案/day17/one.py
請輸入你的年齡:31
請輸入你的城市:上海
True
1.4.3 非(not)
與實際運算結果相反
user_age = int(input('請輸入你的年齡:'))
user_city = input('請輸入你的城市:')
res = not(user_age < 30 or user_city == '上海')
print(res)
執行結果:
C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python37\python.exe E:/python程式小專案/day17/one.py
請輸入你的年齡:31
請輸入你的城市:上海
False
二、Python字串操作
2.1 定義
- 單引號、雙引號:定義單行字串
- 三引號、三雙引號:定義多行字串
- 空字串:s=‘’
- 轉換成字串:str()
注意:字串中有單引號時(外面用雙引號區分;外雙內單,外單內雙,內外一樣用跳脫)
比如: s = "hello,py\"30\"!!"
2.2 索引取值
即通過索引獲取指定位置的字元
2.2.1 順序索引
順序索引的下標是從0開始
s = 'hello,py33'
print(s[0])
print(s[4])
執行結果:
C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python37\python.exe E:/python程式小專案/day17/one.py
h
o
2.2.2 倒序索引
倒序索引的下標是從-1開始
s = 'hello,py33'
s_len = len(s) # 字串長度
print(s[s_len-1]) # 字串長度減1
print(s[-1]) # 倒序,字串最後一位
執行結果:
C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python37\python.exe E:/python程式小專案/day17/one.py
3
3
2.3 索引切片
2.3.1 格式
- 字串[起始索引:結束索引:步長]
- 預設起始索引為0,預設步長為1
- 左閉右開:含起始,不含結束
- 步長為正,表示正序切;步長為負,表示倒序切
- 字串反轉:[::-1] (注意:面試經常會問到這個)
s = "monty,python"
print(s[:3]) # 下標從0開始,結束下標為2,預設步長為1 [0,1,2] 取頭不取尾
print(s[:]) # 下標從0開始,一直到字串最後。步長為1
print(s[2:]) # 下標從2開始,一直到最後。
print(s[::2]) # 下標從0開始,下標+2
print(s[1::2]) # 下標從1開始,下標+2
# 如果步長是正數,正向取。如果步長是負數,倒序取。
print(s[::]) # 全取
print(s[::-1]) # 倒序 - 反轉
執行結果:
C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python37\python.exe E:/python程式小專案/day17/one.py
mon
monty,python
nty,python
mnypto
ot,yhn
monty,python
nohtyp,ytnom
2.4 常見操作
在pycharm中輸入s.之後下拉框會出來
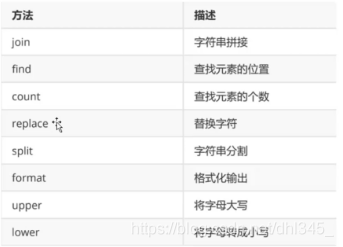
2.4.1 查詢(find)
s = "monty,python"
res = s.find(",") # 引數就是子字串。查詢結果為下標。
print(res)
res = s.find("PY") # 如果找不著,就返回-1
print(res)
res = s.find("py")
print(res)
執行結果:
C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python37\python.exe E:/python程式小專案/day17/one.py
5
-1
6
2.4.2 返回下標(index)
s = "monty,python"
res = s.index("t")
res2 = s.index("t",4)
res3 = s.index("th")
print(res3)
執行結果:
C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python37\python.exe E:/python程式小專案/day17/one.py
8
注意:當查詢的字元不存在於字串之中時,執行結果會報ValueError: substring not found錯誤
2.5 拼接和截斷
2.5.1 split
- 分隔符
- 指定分隔次數
- 預設就是以空格作為分隔符
s = 'keke 九三 數 水滴 小嬋 秋呆呆'
res = s.split(" ")
# res = s.split() # 預設就是以空格作為分隔符
# res = s.split(" ",2) # 執行結果:['keke', '九三', '數 水滴 小嬋 秋呆呆']
print(res)
執行結果:
C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python37\python.exe E:/python程式小專案/day17/one.py
['keke', '九三', '數', '水滴', '小嬋', '秋呆呆']
2.5.2 join
- 列表當中的字串,拼成一個字串。列表當中的成員必須都是字串。
- 以,號將s當中的成員拼成一個字串。
- 用法:拼接符.join(列表) 拼接符也是字串型別。
s = ['keke', '九三', '數', '水滴', '小嬋', '秋呆呆']
new_str = "2 ".join(s)
print(new_str)
執行結果:
C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python37\python.exe E:/python程式小專案/day17/one.py
keke2 九三2 數2 水滴2 小嬋2 秋呆呆
2.5.3 無規則拼接
舉例:隨意拼接兩個字串
s1 = 'hello'
s2 = 'python'
print(s1 + ',' + s2)
執行結果:
C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python37\python.exe E:/python程式小專案/day17/one.py
hello,python
2.6 格式化輸出
2.6.1 format
格式:字串.format():{ }
age = input("請輸入你的年齡:")
height = input("你的身高:")
city = input("你的城市:")
s = "hello,大家好,我今年{}歲!".format(age)
# 用法一 每一個{}都有一個值替換
s1 = "hello,大家好,我今年{}歲,身高{},我在{}".format(age, height, city)
# 用法二
s2 = "hello,大家好,我今年{}歲,身高{},我的大學在{},我的工作城市在{}".format(age, height, city, city)
s3 = "hello,大家好,我今年{0}歲,身高{1},我的大學在{2},我的工作城市在{2}".format(int(age), height, city)
print(s1)
print(s2)
print(s3)
執行結果:
C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python37\python.exe E:/python程式小專案/day17/one.py
請輸入你的年齡:24
你的身高:160
你的城市:成都
hello,大家好,我今年24歲,身高160,我在成都
hello,大家好,我今年24歲,身高160,我的大學在成都,我的工作城市在成都
hello,大家好,我今年24歲,身高160,我的大學在成都,我的工作城市在成都
如果輸出時候的資料需要保留兩位小數點,那麼要使用 .2f
如下:
num1 = 100.236
s = "我今天買了個liulian,價格為{:.2f}".format(num1)
print(s)
執行結果:
C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python37\python.exe E:/python程式小專案/day17/one.py
我今天買了個liulian,價格為100.24
2.6.2 f表示式
f表示式只能在Python3.6以上使用
我個人比較喜歡用這種方式來格式化輸出,比較簡便,但是大家在使用之前一定要確保Python版本是3.6以上,不然會報錯
age = input("請輸入你的年齡:")
height = input("你的身高:")
city = input("你的城市:")
s = f"hello,大家好,我今年{age}歲,身高{height},我在{city}"
print(s)
執行結果:
請輸入你的年齡:24
你的身高:160
你的城市:成都
hello,大家好,我今年24歲,身高160,我在成都
2.6.3 %(只需瞭解)
- %s(格式化字串)
- %d()格式化整數
- %f(格式化浮點數位,可指定小數點後的精度)
age = input("請輸入你的年齡:")
height = input("你的身高:")
city = input("你的城市:")
s = "hello,大家好,我今年%d歲,身高%s,我在%s" % (int(age),height,city)
print(s)
執行結果:
C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python37\python.exe E:/python程式小專案/day17/one.py
請輸入你的年齡:24
你的身高:160
你的城市:成都
hello,大家好,我今年24歲,身高160,我在成都
2.7 跳脫字元
- 換行(\n)
- 輸出一個\,即取消跳脫(\)
print("D:\\Backup\\我的檔案")
print(R'D:\Backup\我的檔案') # 大小r都可以
執行結果:
C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python37\python.exe E:/python程式小專案/day17/one.py
D:\Backup\我的檔案
D:\Backup\我的檔案
跳脫字元還有很多,這裡就寫了兩個常用的,需要看其他的可以去官網檢視具體用法。
這是第二篇學習筆記了,希望大佬們看見了多多指教。