LruCache 的使用及原始碼解析
目錄
在Android 應用中恰當的使用快取技術不僅可以緩解伺服器壓力,還可以優化使用者的使用體驗,減少使用者流量的使用。常用的三級快取主要是指 LruCache、DiskLruCache、網路,其中 LruCache 對應記憶體快取、DiskLruCache 對應磁碟快取。LRU 全稱是 Least Recently Used,即最近最少使用策略,意思是當快取到達限制時候,優先淘汰近期內最少使用的快取,LruCache 和 DiskLruCache 都是採用 LRU 策略。比如說 Android 中常來快取 Bitmap,我們先從 LruCache 中取,取不到再從 DiskLruCache 中取,也取不到的話,最後才從資料來源獲取(網路下載 or 本地檔案)。
記憶體快取的特點:
讀取速度快
可分配空間小
有被系統回收風險
應用退出就沒有了,無法做到離線快取
磁碟快取的特點:
讀取速度比記憶體快取慢
可分配空間較大
不會因為系統記憶體緊張而被系統回收
退出應用快取仍然存在(快取在應用對應的磁碟目錄中解除安裝時會一同清理,快取在其他位置解除安裝會有殘留)
本文主要從原理、使用和原始碼的角度來解析 LruCache。
一、基本原理及底層實現
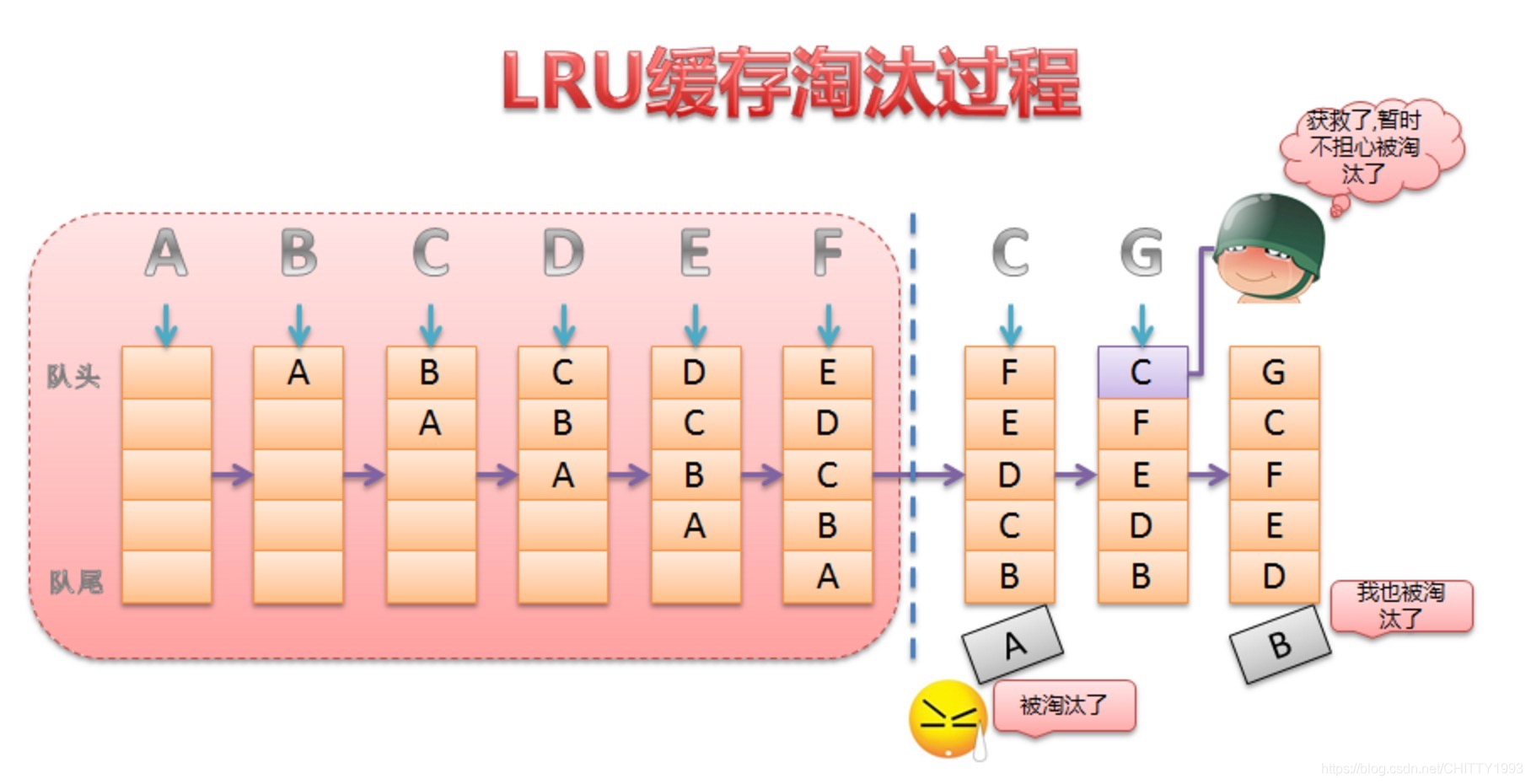
LruCache 使用了 LRU 快取淘汰演演算法,其中 LRU 全稱是 Least Recently Used,即最近最少使用策略。 其底層程式碼實現用到了LinkedHashMap 採用雙向連結串列這種資料結構,是一種空間換時間的設計思想,以及用 synchronized 來保證執行緒安全。並提供了get() 和 put() 方法來完成快取的獲取和新增操作,當快取滿時,LruCache 會移除較早使用的快取物件,然後再新增新的快取物件。來看原始碼註釋瞭解具體的操作過程:
A cache that holds strong references to a limited number of values. Each time a value is accessed, it is moved to the head of a queue. When a value is added to a full cache, the value at the end of that queue is evicted and may become eligible for garbage collection.
一個包含有限數量值的強參照的快取。每次存取一個值,它都會被移動到佇列的頭部。將一個新的值新增到已經滿了的快取佇列時,該佇列末尾的值將會被逐出,並且可能會被垃圾回收機制進行回收。
具體操作過程可看以下圖示:
二、LruCache 的使用
//獲取系統分配給每個應用程式的最大記憶體,單位換算為 KB
int maxMemory=(int)(Runtime.getRuntime().maxMemory()/1024);
int cacheSize=maxMemory/8; //取最大記憶體的 1/8 作為快取容量
private LruCache<String, Bitmap> mMemoryCache;
mMemoryCache = new LruCache<String, Bitmap>(mCacheSize){//給 LruCache 分配快取容量
//重寫該方法,來測量 Bitmap 的大小
@Override
protected int sizeOf(String key, Bitmap bitmap) {
return bitmap.getRowBytes() * value.getHeight()/1024;
}
};
在上面的程式碼中,只需提供快取的總容量大小並重寫 sizeOf() 方法即可。sizeOf() 方法的作用是計算快取物件的大小,這裡大小的單位需要和總容量的單位一致。對於上面的範例程式碼來說,總容量的大小為當前程序的可用記憶體的 1/8,單位為 KB(除以 1024 是為了將其單位轉換為 KB ),而 sizeOf() 方法則完成了 Bitmap 物件的大小計算。一些特殊情況下,還需要重寫 LruCache 的 entryRemoved() 方法,LruCache 移除舊快取時會呼叫 entryRemoved() 方法,因此可以在 entryRemoved() 中完成一些資源回收工作(如果需要的話)。
除了 LruCache 的建立以外,還有快取的獲取和新增,這也很簡單,從LruCache中獲取一個快取物件,如下所示。
三、部分原始碼解析
1. 構造方法
public class LruCache<K, V> {
...
public LruCache(int maxSize) {
if (maxSize <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("maxSize <= 0");
}
this.maxSize = maxSize;
this.map = new LinkedHashMap<K, V>(0, 0.75f, true);
}
}
LruCache 是一個泛型類,從建構函式可以看出,它內部採用了一個 LinkedHashMap 以強參照的方式儲存外界的快取物件,LinkedHashMap 的三個引數分別為 初始容量、載入因子 和 存取順序,當 accessOrder 為 true 時,這個集合的元素順序就會是存取順序,也就是存取了之後就會將這個元素放到集合的最後面(??);false 表示插入順序。
LinkedHashMap 引數介紹:
initialCapacity 用於初始化該 LinkedHashMap 的大小。
loadFactor(負載因子)是 LinkedHashMap 的父類別 HashMap 裡的構造引數,涉及到擴容問題,比如 HashMap 的最大容量是100,那麼這裡設定 0.75f 的話,到 75 的時候就會擴容。
accessOrder 是排序模式,true 表示按照存取順序進行排序( LruCache 核心工作原理就在此),false 表示按照插入的順序進行排序。
有關 LinkedHashMap 的原始碼分析,我們之後另開一篇文章來詳細介紹。這裡先簡單提一下,LinkedHashMap 預設的構造引數是插入順序的,就是說 LinkedHashMap 中儲存的順序是按照呼叫 put() 方法插入的順序進行排序的;而存取順序,是當我們存取了一個 key 後,這個 key 就跑到了隊尾。這裡注意:我們在文章開頭看到 LruCache 原始碼註釋部分介紹的,「Each time a value is accessed, it is moved to the head of a queue. 」 每次存取一個值,它都會被移動到隊頭。那麼被存取的資料到底是被移動到了隊頭還是隊尾呢?帶著疑問我們繼續向下看。
加餐:這裡簡單介紹下上面涉及到的相關知識:強參照、軟參照、弱參照、虛參照的區別。
· 強參照:直接的物件參照;
· 軟參照:當一個物件只有軟參照存在時,系統記憶體不足時此物件會被 gc 回收;
· 弱參照:當一個物件只有弱參照存在時,此物件會隨時被 gc 回收;
· 虛參照:如果一個物件僅持有虛參照,那麼它就和沒有任何參照一樣,在任何時候都可能被垃圾回收。虛參照並不會決定物件的生命週期。虛參照主要用來跟蹤物件被垃圾回收的活動。虛參照必須和參照佇列(ReferenceQueue)聯合使用。
2. LruCahche 的 get() 方法
/**
* Returns the value for {@code key} if it exists in the cache or can be
* created by {@code #create}. If a value was returned, it is moved to the
* head of the queue. This returns null if a value is not cached and cannot
* be created.
*/
public final V get(K key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null");
}
V mapValue;
synchronized (this) {
mapValue = map.get(key);
if (mapValue != null) {
hitCount++;
return mapValue;
}
missCount++;
}
/*
* Attempt to create a value. This may take a long time, and the map
* may be different when create() returns. If a conflicting value was
* added to the map while create() was working, we leave that value in
* the map and release the created value.
* 如果通過 key 從快取集合中獲取不到快取資料,就嘗試使用creat(key) 方法創造一個新資料。
* create(key) 預設返回的也是 null,需要的時候可以重寫這個方法。
*/
V createdValue = create(key);
if (createdValue == null) {
return null;
}
//如果重寫了 create(key) 方法,建立了新的資料,就將新資料放入快取中。
synchronized (this) {
createCount++;
mapValue = map.put(key, createdValue);
if (mapValue != null) {
// There was a conflict so undo that last put
map.put(key, mapValue);
} else {
size += safeSizeOf(key, createdValue);
}
}
if (mapValue != null) {
entryRemoved(false, key, createdValue, mapValue);
return mapValue;
} else {
trimToSize(maxSize);
return createdValue;
}
}
從 get() 方法的註釋中我們可以看到,如果一個 key 存在於快取中,或者其可以由 create() 建立,則返回 key 的值。如果返回了一個值,它將移動到佇列的頭部。如果值未快取且無法建立,則返回 null。從而解答了我們上面的疑惑,被存取的元素會移動到佇列的頭部,而佇列的尾部元素是最近最少使用的元素。
3. LruCache 的 put() 方法
/**
* Caches {@code value} for {@code key}. The value is moved to the head of
* the queue.
*
* @return the previous value mapped by {@code key}.
*/
public final V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null || value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null || value == null");
}
V previous;
synchronized (this) {
putCount++;
//safeSizeOf(key, value)。
//safeSizeOf() 方法內呼叫了 sizeOf() 方法,sizeOf() 方法預設返回1,也就是將快取的個數加1.
// 當快取的是圖片的時候,這個 size 應該表示圖片佔用的記憶體的大小,所以應該重寫裡面呼叫的 sizeOf(key, value)
size += safeSizeOf(key, value);
//向 map 中加入快取物件,若快取中已存在,返回已有的值,否則執行插入新的資料
previous = map.put(key, value);
//如果已有快取物件,則快取大小恢復到之前
if (previous != null) {
size -= safeSizeOf(key, previous);
}
}
//entryRemoved() 是個空方法,可以自行實現
if (previous != null) {
entryRemoved(false, key, previous, value);
}
//通過 trimToSize() 方法 來判斷 size 是否大於 maxSize。
trimToSize(maxSize);
return previous;
}
可見,put() 方法就是新增快取物件,以及在新增過快取物件後,呼叫 trimToSize() 方法,來判斷加入元素後是否超過最大快取數,如果超過就要清除掉近期最少使用的元素。其原始碼如下
/**
* Remove the eldest entries until the total of remaining entries is at or
* below the requested size.
*
* @param maxSize the maximum size of the cache before returning. May be -1
* to evict even 0-sized elements.
*/
public void trimToSize(int maxSize) {
while (true) {
K key;
V value;
synchronized (this) {
//如果 map 為空並且快取 size 不等於 0 或者快取 size 小於 0 ,丟擲異常
if (size < 0 || (map.isEmpty() && size != 0)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(getClass().getName()
+ ".sizeOf() is reporting inconsistent results!");
}
//如果快取 size 小於最大快取,不需要再刪除快取物件,跳出迴圈
if (size <= maxSize) {
break;
}
//在快取佇列中查詢最近最少使用的元素,若不存在,直接退出迴圈,若存在則在 map 中刪除該元素
Map.Entry<K, V> toEvict = map.eldest();
if (toEvict == null) {
break;
}
key = toEvict.getKey();
value = toEvict.getValue();
map.remove(key);
size -= safeSizeOf(key, value);
//回收次數 +1
evictionCount++;
}
entryRemoved(true, key, value, null);
}
}
4. LruCache 的 remove() 方法
/**
* Removes the entry for {@code key} if it exists.
*
* @return the previous value mapped by {@code key}.
*/
public final V remove(K key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null");
}
V previous;
synchronized (this) {
previous = map.remove(key);
if (previous != null) {
size -= safeSizeOf(key, previous);
}
}
if (previous != null) {
entryRemoved(false, key, previous, null);
}
return previous;
}
其內部呼叫了 entryRemoved() 的方法來實現從快取中刪除內容,並更新快取大小。
四、LeetCode :LruCache 快取機制。
大家可以去力扣練習並熟練掌握其中一種解法。敲重點!!此題有大廠面試要求手寫哦~
五、LruCache 的官方檔案和完整原始碼謄錄
/*
* Copyright (C) 2011 The Android Open Source Project
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package android.util;
import android.compat.annotation.UnsupportedAppUsage;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* A cache that holds strong references to a limited number of values. Each time
* a value is accessed, it is moved to the head of a queue. When a value is
* added to a full cache, the value at the end of that queue is evicted and may
* become eligible for garbage collection.
*
* <p>If your cached values hold resources that need to be explicitly released,
* override {@link #entryRemoved}.
*
* <p>If a cache miss should be computed on demand for the corresponding keys,
* override {@link #create}. This simplifies the calling code, allowing it to
* assume a value will always be returned, even when there's a cache miss.
*
* <p>By default, the cache size is measured in the number of entries. Override
* {@link #sizeOf} to size the cache in different units. For example, this cache
* is limited to 4MiB of bitmaps:
* <pre> {@code
* int cacheSize = 4 * 1024 * 1024; // 4MiB
* LruCache<String, Bitmap> bitmapCache = new LruCache<String, Bitmap>(cacheSize) {
* protected int sizeOf(String key, Bitmap value) {
* return value.getByteCount();
* }
* }}</pre>
*
* <p>This class is thread-safe. Perform multiple cache operations atomically by
* synchronizing on the cache: <pre> {@code
* synchronized (cache) {
* if (cache.get(key) == null) {
* cache.put(key, value);
* }
* }}</pre>
*
* <p>This class does not allow null to be used as a key or value. A return
* value of null from {@link #get}, {@link #put} or {@link #remove} is
* unambiguous: the key was not in the cache.
*
* <p>This class appeared in Android 3.1 (Honeycomb MR1); it's available as part
* of <a href="http://developer.android.com/sdk/compatibility-library.html">Android's
* Support Package</a> for earlier releases.
*/
public class LruCache<K, V> {
@UnsupportedAppUsage
private final LinkedHashMap<K, V> map;
/** Size of this cache in units. Not necessarily the number of elements. */
private int size;
private int maxSize;
private int putCount;
private int createCount;
private int evictionCount;
private int hitCount;
private int missCount;
/**
* @param maxSize for caches that do not override {@link #sizeOf}, this is
* the maximum number of entries in the cache. For all other caches,
* this is the maximum sum of the sizes of the entries in this cache.
*/
public LruCache(int maxSize) {
if (maxSize <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("maxSize <= 0");
}
this.maxSize = maxSize;
this.map = new LinkedHashMap<K, V>(0, 0.75f, true);
}
/**
* Sets the size of the cache.
*
* @param maxSize The new maximum size.
*/
public void resize(int maxSize) {
if (maxSize <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("maxSize <= 0");
}
synchronized (this) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
}
trimToSize(maxSize);
}
/**
* Returns the value for {@code key} if it exists in the cache or can be
* created by {@code #create}. If a value was returned, it is moved to the
* head of the queue. This returns null if a value is not cached and cannot
* be created.
*/
public final V get(K key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null");
}
V mapValue;
synchronized (this) {
mapValue = map.get(key);
if (mapValue != null) {
hitCount++;
return mapValue;
}
missCount++;
}
/*
* Attempt to create a value. This may take a long time, and the map
* may be different when create() returns. If a conflicting value was
* added to the map while create() was working, we leave that value in
* the map and release the created value.
*/
V createdValue = create(key);
if (createdValue == null) {
return null;
}
synchronized (this) {
createCount++;
mapValue = map.put(key, createdValue);
if (mapValue != null) {
// There was a conflict so undo that last put
map.put(key, mapValue);
} else {
size += safeSizeOf(key, createdValue);
}
}
if (mapValue != null) {
entryRemoved(false, key, createdValue, mapValue);
return mapValue;
} else {
trimToSize(maxSize);
return createdValue;
}
}
/**
* Caches {@code value} for {@code key}. The value is moved to the head of
* the queue.
*
* @return the previous value mapped by {@code key}.
*/
public final V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null || value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null || value == null");
}
V previous;
synchronized (this) {
putCount++;
size += safeSizeOf(key, value);
previous = map.put(key, value);
if (previous != null) {
size -= safeSizeOf(key, previous);
}
}
if (previous != null) {
entryRemoved(false, key, previous, value);
}
trimToSize(maxSize);
return previous;
}
/**
* Remove the eldest entries until the total of remaining entries is at or
* below the requested size.
*
* @param maxSize the maximum size of the cache before returning. May be -1
* to evict even 0-sized elements.
*/
public void trimToSize(int maxSize) {
while (true) {
K key;
V value;
synchronized (this) {
if (size < 0 || (map.isEmpty() && size != 0)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(getClass().getName()
+ ".sizeOf() is reporting inconsistent results!");
}
if (size <= maxSize) {
break;
}
Map.Entry<K, V> toEvict = map.eldest();
if (toEvict == null) {
break;
}
key = toEvict.getKey();
value = toEvict.getValue();
map.remove(key);
size -= safeSizeOf(key, value);
evictionCount++;
}
entryRemoved(true, key, value, null);
}
}
/**
* Removes the entry for {@code key} if it exists.
*
* @return the previous value mapped by {@code key}.
*/
public final V remove(K key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null");
}
V previous;
synchronized (this) {
previous = map.remove(key);
if (previous != null) {
size -= safeSizeOf(key, previous);
}
}
if (previous != null) {
entryRemoved(false, key, previous, null);
}
return previous;
}
/**
* Called for entries that have been evicted or removed. This method is
* invoked when a value is evicted to make space, removed by a call to
* {@link #remove}, or replaced by a call to {@link #put}. The default
* implementation does nothing.
*
* <p>The method is called without synchronization: other threads may
* access the cache while this method is executing.
*
* @param evicted true if the entry is being removed to make space, false
* if the removal was caused by a {@link #put} or {@link #remove}.
* @param newValue the new value for {@code key}, if it exists. If non-null,
* this removal was caused by a {@link #put} or a {@link #get}. Otherwise it was caused by
* an eviction or a {@link #remove}.
*/
protected void entryRemoved(boolean evicted, K key, V oldValue, V newValue) {}
/**
* Called after a cache miss to compute a value for the corresponding key.
* Returns the computed value or null if no value can be computed. The
* default implementation returns null.
*
* <p>The method is called without synchronization: other threads may
* access the cache while this method is executing.
*
* <p>If a value for {@code key} exists in the cache when this method
* returns, the created value will be released with {@link #entryRemoved}
* and discarded. This can occur when multiple threads request the same key
* at the same time (causing multiple values to be created), or when one
* thread calls {@link #put} while another is creating a value for the same
* key.
*/
protected V create(K key) {
return null;
}
private int safeSizeOf(K key, V value) {
int result = sizeOf(key, value);
if (result < 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Negative size: " + key + "=" + value);
}
return result;
}
/**
* Returns the size of the entry for {@code key} and {@code value} in
* user-defined units. The default implementation returns 1 so that size
* is the number of entries and max size is the maximum number of entries.
*
* <p>An entry's size must not change while it is in the cache.
*/
protected int sizeOf(K key, V value) {
return 1;
}
/**
* Clear the cache, calling {@link #entryRemoved} on each removed entry.
*/
public final void evictAll() {
trimToSize(-1); // -1 will evict 0-sized elements
}
/**
* For caches that do not override {@link #sizeOf}, this returns the number
* of entries in the cache. For all other caches, this returns the sum of
* the sizes of the entries in this cache.
*/
public synchronized final int size() {
return size;
}
/**
* For caches that do not override {@link #sizeOf}, this returns the maximum
* number of entries in the cache. For all other caches, this returns the
* maximum sum of the sizes of the entries in this cache.
*/
public synchronized final int maxSize() {
return maxSize;
}
/**
* Returns the number of times {@link #get} returned a value that was
* already present in the cache.
*/
public synchronized final int hitCount() {
return hitCount;
}
/**
* Returns the number of times {@link #get} returned null or required a new
* value to be created.
*/
public synchronized final int missCount() {
return missCount;
}
/**
* Returns the number of times {@link #create(Object)} returned a value.
*/
public synchronized final int createCount() {
return createCount;
}
/**
* Returns the number of times {@link #put} was called.
*/
public synchronized final int putCount() {
return putCount;
}
/**
* Returns the number of values that have been evicted.
*/
public synchronized final int evictionCount() {
return evictionCount;
}
/**
* Returns a copy of the current contents of the cache, ordered from least
* recently accessed to most recently accessed.
*/
public synchronized final Map<K, V> snapshot() {
return new LinkedHashMap<K, V>(map);
}
@Override public synchronized final String toString() {
int accesses = hitCount + missCount;
int hitPercent = accesses != 0 ? (100 * hitCount / accesses) : 0;
return String.format("LruCache[maxSize=%d,hits=%d,misses=%d,hitRate=%d%%]",
maxSize, hitCount, missCount, hitPercent);
}
}